Uncultured microbial phyla suggest mechanisms for multi-thousand-year subsistence in Baltic Sea sediments
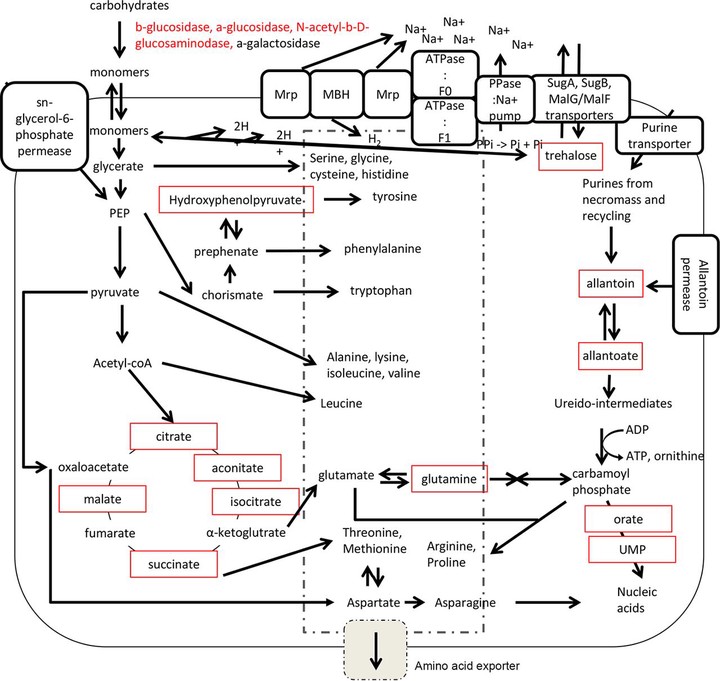 Figure 6: Unique attributes of Atribacteria provide advantages in energy-limited marine sediments.
Figure 6: Unique attributes of Atribacteria provide advantages in energy-limited marine sediments.
Abstract
Energy-starved microbes in deep marine sediments subsist at near-zero growth for thousands of years, yet the mechanisms for their subsistence are unknown because no model strains have been cultivated from most of these groups. We investigated Baltic Sea sediments with single-cell genomics, metabolomics, metatranscriptomics, and enzyme assays to identify possible subsistence mechanisms employed by uncultured Atribacteria, Aminicenantes, Actinobacteria group OPB41, Aerophobetes, Chloroflexi, Deltaproteobacteria, Desulfatiglans, Bathyarchaeota, and Euryarchaeota marine group II lineages. Some functions appeared to be shared by multiple lineages, such as trehalose production and NAD+-consuming deacetylation, both of which have been shown to increase cellular life spans in other organisms by stabilizing proteins and nucleic acids, respectively. Other possible subsistence mechanisms differed between lineages, possibly providing them different physiological niches. Enzyme assays and transcripts suggested that Atribacteria and Actinobacteria group OPB41 catabolized sugars, whereas Aminicenantes and Atribacteria catabolized peptides. Metabolite and transcript data suggested that Atribacteria utilized allantoin, possibly as an energetic substrate or chemical protectant, and also possessed energy-efficient sodium pumps. Atribacteria single-cell amplified genomes (SAGs) recruited transcripts for full pathways for the production of all 20 canonical amino acids, and the gene for amino acid exporter YddG was one of their most highly transcribed genes, suggesting that they may benefit from metabolic interdependence with other cells. Subsistence of uncultured phyla in deep subsurface sediments may occur through shared strategies of using chemical protectants for biomolecular stabilization, but also by differentiating into physiological niches and metabolic interdependencies.